A CNAME (Canonical Name) record is a name that refers to another name. Technically, this can be called an alias – the same address is accessible through several names.
A more common use is related to the outdated website name www.domainname.ee. WWW is actually a subdomain of domainname.ee. In order for a web site starting with www to be accessible, a CNAME record is established which indicates that www.domainname.ee points to domainname.ee, which in turn has an A record with the IP address of the web server. It doesn’t matter whether a website visitor is looking for the address www.domainname.ee or domainname.ee, in both cases they end up on your site.
A CNAME record is recommended when multiple different hosts are pointing to the same IP address. Different services can run on the same server, such as a web server and an FTP server. In this case, the CNAME record created for FTP points from ftp.domainname.ee to domainname.ee.
ANAME – Alias name
If in order to use a web service you need to contact the server of your domain name service provider and only the (sub)domain provided by the service provider is suitable for this, a combination of CNAME and URL can be used for this purpose.
This domain name forwarding is also known as Alias name, abbreviated as ANAME.
If in order to use a web service you need to contact the server of your domain name.ee service provider and only the (sub)domain provided by the service provider is suitable for this, a combination of CNAME and URL can be used for this purpose.
This domain name forwarding is also known as Alias name, abbreviated as ANAME.
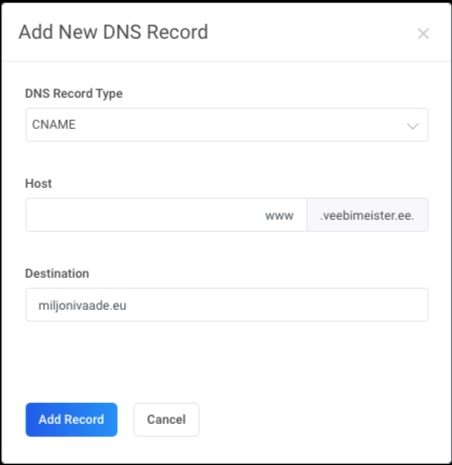
Example: Add a following CNAME record
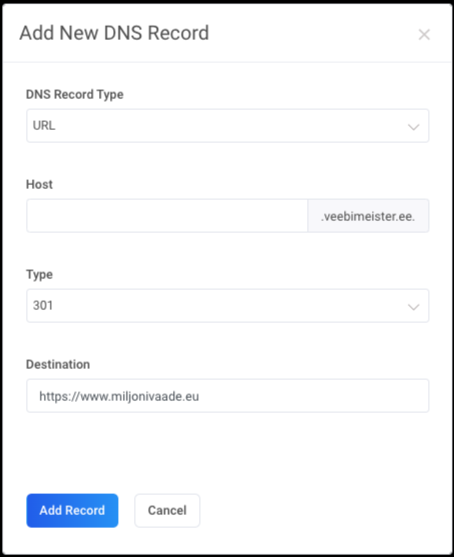
and to access the domain provided by the service provider through a second-level domain, add a following URL record.
Additional information: Redirecting domain using URL records